NSW to Run Out of Gas by 2028

You might have heard that New South Wales (NSW) could face a critical gas shortage as early as 2028. This isn't a distant threat; it's a looming reality that could significantly impact homes and businesses across the state. Understanding the implications of the gas shortage forecast is crucial, especially now when ensuring a reliable energy supply is of utmost importance. Let's break down what's happening and explore what this means for you.
The Problem: Not Enough Gas to Go Around
EnergyQuest’s annual in depth analysis report has raised serious concerns about NSW's future gas supply. The combination of reduced local gas production and increased demand is leading industry analysts and energy experts to anticipate a potential supply shortfall
According to the Australian Energy Market Operator’s (AEMO) recent assessment, the current trajectory suggests a significant supply gap by 2028. Key figures highlight the rapid depletion of existing gas reserves and the challenges of securing alternative sources.
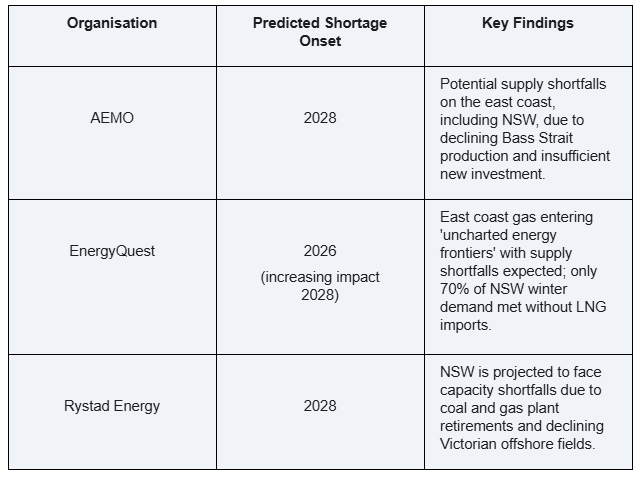
The following table provides a clear overview of the predictions of Australia’s key organisations’ forecasts for the NSW gas shortage:
How Will the Gas Crisis Affect You?
This gas shortage could hit us in a few ways :
💲 Higher Prices
Gas prices could go up, making your energy bills more expensive. This affects everyone, from families to businesses .
📉 Business Troubles
Businesses that use a lot of gas, like factories and even your local bakery, might struggle with higher costs. Some might even have to close down, leading to job losses . We're already seeing some businesses put off hiring or expanding because of current gas prices .
🥶 Everyday Life
Many homes in NSW use gas for cooking and heating. If there's a shortage and prices go up, things like staying warm in winter could become more expensive .
Is There a Solution?
Luckily, there are some ideas on how to tackle this problem:
1️⃣ Bringing in Gas from Overseas: A new terminal at Port Kembla could allow NSW to import liquified natural gas (LNG) from other countries. This could help make sure we have enough gas and keep prices stable.
2️⃣ Government Plans: The government is working on a "Future Gas Strategy" to figure out how to best manage gas supplies . They're also looking at ways to use less gas in the long run.
3️⃣ Renewable Power: The big picture solution is to move towards cleaner energy like solar and wind. The more we use renewable energy, the less we'll need gas.

LNG Terminals - Are They The Answer?
As NSW faces the prospect of a gas shortage, the question of LNG terminals inevitably arises. These facilities, designed to import and regasify LNG from overseas, are touted by some as a potential solution to bridge the supply gap.
The Potential Benefits
👍 Diversification of Supply
LNG terminals could offer NSW access to a broader range of gas suppliers, reducing reliance on domestic production and interstate pipelines.
👍 Increased Supply Security
In theory, LNG imports could provide a more stable and predictable gas supply, mitigating the risks associated with fluctuating domestic production.
👍 Addressing Short Term Gaps
LNG could serve as a stop gap measure, to help alleviate immediate supply constraints while the transition to renewable energy progresses.
LNG Challenges and Concerns
👎 Environmental Impact
LNG extraction and transport contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, potentially undermining NSW's climate goals. There are also concerns about the environmental impact of building and operating LNG terminals, including potential damage to marine ecosystems.
👎 Price Volatility
LNG prices are subject to global market fluctuations, which could lead to significant price increases for consumers in NSW. Global events can also drastically affect the price of LNG.
👎 Infrastructure Costs
Building and operating LNG terminals requires investment, which could ultimately be passed on to consumers.
👎 Long Lead Times
Developing and constructing LNG terminals is a lengthy process, meaning they may not be a viable solution for addressing the immediate supply challenges.
👎 Community Concerns
There is strong local opposition to LNG terminal developments due to environmental and safety concerns.
👎 Fossil Fuel Lock In
Investing heavily in LNG infrastructure could increase reliance on fossil fuels, hampering the transition to cleaner energy sources.
Why Campaigners Say "No" to LNG Terminals
Campaigners against new LNG terminals argue that it's ridiculous for Australia, a major gas exporter second only to the United States, to consider becoming a gas importer. This would only further expose Australians to the volatility of global gas markets and drive up our energy bills.
Given that most Australian gas exports originate from Queensland and Western Australia, and Queensland's LNG producers aren't obligated to reserve any gas for domestic use, a policy shift could significantly reduce the need for costly LNG imports and the construction of numerous import terminals.

Does the “Future Gas Strategy” Provide a Realistic Plan?
The Future Gas Strategy (FGS), often promoted by governments and industry, aims to ensure a continued role for natural gas in the energy mix. However, its effectiveness and long term viability are subject to debate. Here's a breakdown of the key pros and cons:
The Future Gas Strategy, which supports a continued role of natural gas, raises critical questions about its viability in addressing the gas crisis. Here's a look at the strategy's pros and cons, specifically in the context of this 2028 deadline:
FGS Pros
👍 The FGS Ambition
Pro-FGS supporters might argue that if the strategy is implemented swiftly, it could theoretically boost gas supplies before 2028. This would rely heavily on rapid development of new gas fields or expedited LNG import solutions.
The idea being, to have something in place before the predicted shortfall.
👍 Short Term Focus: Maintaining Existing Industrial Base
For industries heavily reliant on gas, the strategy offers the promise of continued operations, potentially reducing the immediate economic disruption leading up to 2028. This is a just short term approach, to keep industry going until other solutions are found.
Cons: The Reality
👎 Time Constraints
Developing new gas fields or building LNG terminals takes years. The 2028 deadline leaves little room for error, making these solutions highly risky. The time to build the needed infrastructure is realistically just too long.
👎 Climate Risks
Even if the strategy addresses the supply gap in the short term, it risks locking NSW into a fossil fuel future, ruining the state's climate goals and worsening the impacts of climate change beyond 2028. Ergo, the long term climate damage outweighs any short term gain.
👎 Financial Risks
Investing heavily in gas infrastructure with a short term timeframe, there would be significant financial risks and a high chance of wasting taxpayer’s money. If the move to renewables accelerates, these investments could become stranded assets, leaving NSW with an expensive burden.
👎 Competition for Funds
Investing in and promoting gas infrastructure can divert resources and attention away from the development and deployment of renewable energy technologies and energy storage solutions. Essentially, every dollar spent on gas is a dollar not spent on renewable energy.
👎 Price Volatility
Even if the strategy succeeds in boosting supply, NSW would still be exposed to volatile gas prices and supply disruptions, particularly if reliant on international LNG markets. The problem would just be transferred, not resolved.
Is the Transition to Renewable Energy Sustainable?
As NSW struggles with the prospect of a gas shortage by 2028, a basic question arises: can the ongoing transition to renewable energy truly fill the capacity gap and provide a reliable, sustainable power supply? This is a complex issue with valid points on both sides, requiring a realistic assessment of the challenges and opportunities.
The transition to renewable energy is not without its difficulties, but it is a necessary and achievable goal. While the 2028 deadline for the NSW gas shortage presents a significant priority, it also emphasises the importance of rushing the move to renewables.
With strategic planning, continued investment, and technological innovation, renewable energy can sustainably and reliably meet the capacity needs of NSW and contribute to a cleaner, more secure energy future. It's not a simple switch, but a carefully managed evolution that requires commitment and planning.
So, What Needs to Happen?
Experts agree that we need to act fast. We need to build the right infrastructure, like the import terminal, and make smart choices about our energy use. Investing in renewable energy and finding ways to be more energy efficient are key to a stable and affordable energy future for NSW .
In short: NSW is facing a gas problem, but there are solutions. By looking at different ways to get gas and focusing on cleaner energy, we can hopefully avoid the worst of the predicted shortages.
To discuss your energy options or transitioning away from gas in your home or business, call Powerix today on 1300 856 928.
Resources:
Energy Quest - East Coast Gas Outlook 2024
NSW Government - Future of Gas Statement
Rystad Energy - Australia’s nuclear debate to shape election, but immediate energy security hinges on gas
9 News - Is Australia running out of gas?
Sydney Morning Herald - ‘Time is running out’: Victoria, NSW turn to gas imports as energy crisis nears
Financial Review - Santos, AEMO issue warnings on gas
Squadron Energy - PKETis Australia's Answer to Looming Gas Shortage
Gas Outlook - Australia’s gas supply conundrum continues amid shortage warnings
ABC News - Gas shortages could soon be a reality on Australia's east coast
